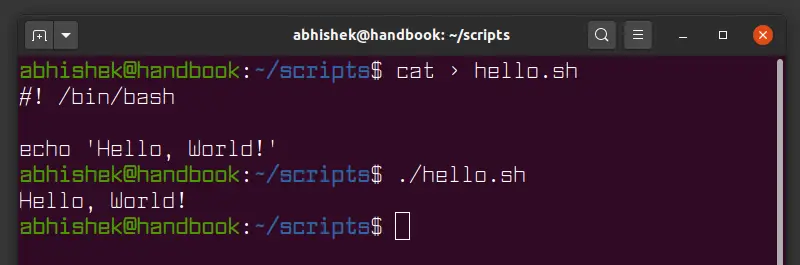
Another way to use the "while" loop in a bash script is without any condition mentioned within it. So, after adding the bash extension in the same file, "bash.sh", we have initialized a "while" loop with no conditions. Within the "do" clause of a "while" loop, the read statement is used to get input from the user in two variables, "x" and "y".
The variable "z" has been initialized, which is taking the sum of both variables "x" and "y" as its value. After this, we have used the "if" statement to check a condition that if a value of variable "x" equals the 5, the "do" statement will be printed out. Within the "do" clause, the echo statement will be printed out, and the loop will be broken. Many of us heard about and may even have tried many of the loops and statements in the programming world.
Many types of loops exist in programming languages, one of them is the "while" loop. This loop is used to execute the number of lines in its "do" clause when the condition is satisfied. Let's see some examples of using the "while" loop with different syntaxes in the bash script. In the initialization part, any variables needed are declared . If multiple variables are declared, they should all be of the same type.
The condition part checks a certain condition and exits the loop if false, even if the loop is never executed. If the condition is true, then the lines of code inside the loop are executed. The advancement to the next iteration part is performed exactly once every time the loop ends. The loop is then repeated if the condition evaluates to true. With Bash, you can do many of the same things you would do in other scripting or programming languages.
You can create and use variables, execute loops, use conditional logic, and store data in arrays. The second method to use the while loop in the bash script is with the square brackets. So, let's open the same file once again to update its code. After the bash extension, we have added a variable "z" with a value of 1. The "while" loop has been initialized with the condition in its square brackets.
If the value of "z" is less than 10, it will execute the "do" clause. The do clause contains an "echo" statement to print out the variable value and increment it with 1. A while loop in bash consists of a conditional expression and a loop body which is surrounded by do and done.
The loop body continues to be executed as long as the condition evaluates to true. The conditional expression in while loop can be surrounded by either a pair of single square brackets or a pair of double round brackets. Depending on whether you are using square brackets or round brackets, the type of operators you are allowed to use vary, as illustrated below. Also note that there should be spaces between opening/closing brackets and the conditional-expression. The scripting language is similar to REXX in implementation.
Mathematical operations are supported on script variables. Flow control is achieved viaif/else/endif and while/endwhileconstructs. Loop flow may be modified by the continue orbreak commands. Strings contained in variables or generated via an expression may be issued to GrADS as commands. The output from those commands (i.e., the text that GrADS would have output to the terminal) is put into a variable and made available to the script.
In this course, you'll learn how to generate some random data, including how to automate the process of generating a random password. Finally, we'll walk you through how to add users to a Linux system. When braces are used for grouping, the newline is not treated as the end of a Tcl command. This makes it simpler to write multiple line commands. However, the opening bracemust be on the line with the for command, or the Tcl interpreter will treat the close of the next brace as the end of the command, and you will get an error. This is different than other languages like C or Perl, where it doesn't matter where you place your braces.
The functionality of the while loop is similar to for loop. The for loop iterates over a list of items and runs the block of code N a number of times. Here in the while loop, the condition is evaluated first, and if the condition is true, the block of code will be executed until the condition is evaluated to false.
The name for-loop comes from the word for, which is used as the keyword in many programming languages to introduce a for-loop. As we can see the continue statement, jumps to the beginning of the block and starts the execution of the commands by skipping the next commands inside the block. This is done to avoid logging of every number and only print the numbers which do not follow a pattern or condition in the if statement or other conditional statements. We can use the continue statement to do the opposite of the break statement. It will jump to the start of the loop block and iterate again. This can be used for skipping over certain commands for certain conditions and hence allows a change in the flow of the loop.
From the script and the execution, we can see that we were able to break or exit an infinite loop with a conditional statement and the break statement. Thus the break statement is used to get the control flow of a program/script from inside a while loop to break out of the loop without the loop condition evaluating to true. We use break statements to exit out of the loop without waiting for the condition of the while loop to evaluate to true. This can be used to exit out of an infinite loop with a programmatic condition inside the loop and thus maintain the control of the loop. Within the file, add the bash extension first at the top of a file. The while loop has been initialized to check the condition for variable "z".
If the value of "z" is equal to or less than 10, the "do" clause will be executed. Within the "do" clause, the value of variable "z" will be displayed with the help of the "echo" statement. Also, the variable "z" value would be incremented by 2. Awk looping statements are used for performing set of actions again and again in succession. It repeatedly executes a statement as long as condition is true.
Awk has number of looping statement as like 'C' programming language. Both the for and while statements allow you to express a loop with a terminating condition (i.e., run the loop while the condition is true). The for statement is more versatile than the while statement as you can also iterate over a list of items using a for loop without explicitly defining a condition.
Thus for loops are often used when the number of loop iterations or the items to iterate over are already known. These are very small tasks and can be easily covered using bash scripts and while loop works like a charm in many such situations. This article is all about how to read files in bash scripts using a while loop. You should be familiar with different methods and which method is more efficient to use. In bash, a single task can be achieved in many ways but there is always an optimal way to get the task done and we should follow it.
The while loop is mostly used when you have to read the contents of the file and further process it. Reading and writing to a file are common operations when you write bash scripts. The select command is a particular case because it is not a primary Bash scripting loop. Use the continue statement to provide a different output based on the user-selected value.
If the condition is false then the commands inside the while block are executed and are iterated again after checking the condition. Also if the condition is true the statements inside the while block are skipped and the statements after the while block are executed. — Awk while loop checks the condition first, if the condition is true, then it executes the list of actions.
After action execution has been completed, condition is checked again, and if it is true, actions is performed again. If the condition returns false in the first iteration then actions are never executed. During evaluation of the forcommand, the start code is evaluated once, before any other arguments are evaluated.
After the start code has been evaluated, the test is evaluated. If the test evaluates to true, then the body is evaluated, and finally, the next argument is evaluated. After evaluating the nextargument, the interpreter loops back to the test, and repeats the process. If the test evaluates as false, then the loop will exit immediately. That is, a value is assigned to the loop variable i and only if the while expression is true will the loop body be executed. If the result were false the for-loop's execution stops short.
Looping allows you to iterate over a list or a group of values until a specific condition is met. In this article, let us review about awk loop statements – while, do while, for loops, break, continue, and exit statements along with 7 practical examples. Similar to for and while, the until statement allows you to define a conditional loop.
However, the difference of until lies in how the condition is handled. The for/while loops are executed while the condition is true. On the other hand, until loops are iterated until the condition is true, meaning that the loops are executed while the condition is false.
Blank Line Not IgnoredSee the result, blank line is not ignored. Also, an interesting thing to note is how white spaces are trimmed by the read command. A simple way to ignore blank lines when reading the file content is to use the test operator with the -z flag which checks if the string length is zero. Now let's repeat the same example but this time with a test operator. To create infinite loops, you can use the bash-builtin true keyword.
Also, use the "sleep" command when testing infinite loops which will give you control in stopping the script else your screen will be flooded with fast scrolling outputs. The given set of items can be a literal set of objects or anything that Bash can extrapolate to a list. For example, text pulled from a file, the output of another Bash command, or parameters passed via the command line. Converting this loop structure into a Bash script is also trivial. What we're doing here is setting our variable to have an initial value of 1.
When the loop begins, our variable is 1 (i.e. less than 3) and so the condition returns true. That means that we're going to execute the code body, returning our variable value, 1 to the terminal. Next, we increment our variable value from 1 to 2 using the ++ notation. This continues while our variable has a value less than or equal to 3. We can use the while loop to iterate till we manually exit out of the loop using CTRL + D by saving changes to the file or by CTRL + C for avoiding writing to the file. We use the read command to input the text from the command line and parse it to the file.
We can use get ops options to read the input from the command line and if there are multiple arguments, we can check them and parse them one by one using a while loop. A while loop is a statement that iterates over a block of code till the condition specified is evaluated to true. We can use this statement or loop in our program when do not know how many times the condition is going to evaluate to false before evaluating to true.
After adding the bash extension, we have declared a variable "file" containing the path to a file. The "while" loop has been initialized to read the file data. If the file has permissions to be read out as the flag "-r" indicates, then each line from the file would be read out using the "echo" statement within the "do" clause. In addition to while, we can also use the until loop which is very similar to the while loop.
The syntax of the until loop is the same as the while loop, however the main difference is that the condition is opposite to that of while. Here the loop commands are executed every time the condition fails, or returns false. Looping is a fundamental idea in programming that will be pretty useful in multitasking tasks. We may use numerous functions such as for, while, and until to loop in bash scripting. – Awk Do while loop is called exit controlled loop, whereas awk while loop is called as entry controlled loop.
Because while loop checks the condition first, then it decides to execute the body or not. But the awk do while loop executes the body once, then repeats the body as long as the condition is true. This is a simple enough loop to not need detailed coverage at present.
As we move ahead with topics, we'll continue to use the while loop on a consistent basis. For more detailed operations including reading files, evaluating more conditions, etc. When you follow through with the shell scripting 101 tutorials, you will learn one topic with every tutorial. Make sure you practice enough to make sure you're well versed and have a good hands-on before moving to the next topic. In this tutorial, we've covered the while loop in shell script and the usage.
A while loop in shell scripts is used to repeat instructions multiple times until the condition for the loop stays true. Loops have a lot of use cases in real-world applications since we create them to automate repetitive tasks. Let's go over some of the use cases and learn to use the while loop in shell scripts. This time our echo statement outside the loop was executed, so you should know when to use exit and break statement. Most programming languages support various forms of looping code lines. Bash natively supports 'while' loops, 'until' loops and the most well-known, 'for' loops.


























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.